Reading: Equality of Opportunity
Equality
of Opportunity
•Equality
of opportunity says that a distribution is just if, and only if, it assigns
positions in society according to morally relevant criteria such as ability or
merit and not according to morally arbitrary criteria, such as gender or race.
•People
should get the position they deserve based on ability and past performance.
•Often
used in business decisions regarding employees, suppliers, and customer.
Problems
with Equality of Opportunity
•Ability,
effort, merit, and desert are often determined by factors that are arbitrary
from a moral point of view.
- Genetic lottery
- Family background
- Lucky decisions
- Genetic lottery
- Family background
- Lucky decisions
•How
should benefits be distributed to positions?
•Usual
answer is according to marginal contribution
Desert
= Marginal Contribution: The Pin Factory
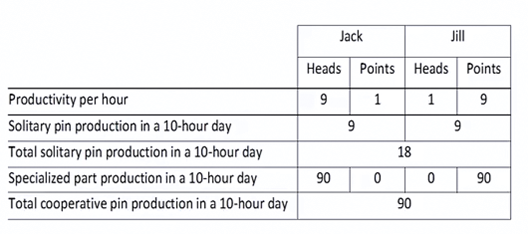
Measuring
Marginal Contribution: The Pin Factory
•Together,
Jack and Jill will produce 90 pins per day.
•Without
Jill, Jack can only produce 9 pins per day.
•Jill’s
marginal contribution is 81 pins (90-9 = 81).
•Therefore,
Jill deserves 81 pins.
•Without
Jack, Jill can only produce 9 pins per day.
•Jack’s
marginal contribution is 81 pins.
•81+81
= 162, however there are only 90 pins
•RAA
Marginal
Contribution in a Firm
Equality
of Welfare
•Equality
of welfare holds that a distribution of property rights in resources is just
if, and only if, it results in everyone having the same level of welfare.
•Problem:
measuring and comparing welfare
•Problem:
expensive tastes. Appears to say that we should justify the preferences of
those who do not enjoy inexpensive resources.
•Problem:
leveling down. Appears to say that we should reduce everyone to the same level
of preference satisfaction
Last modified: Tuesday, August 14, 2018, 10:16 AM
