Reading: Marketing Planning Process
Elements
of Marketing Planning
•Marketing
does not take place in a vacuum.
•A
mission statement articulates an organization’s purpose, or reason for
existence.
•Most
mission statements also include a discussion of what the company would like to
become in the future – its strategic vision.
Elements
of Marketing Planning
•Goals
eventually become refined into specific measurable, and (hopefully) attainable
objectives for the firm.
Organizational
Strategies
•A
strategy is a comprehensive plan stating how the organization will achieve its
mission and objective.
•A
firm’s generic strategy is its overall directional strategy at the business
level.
Elements
of Marketing Planning
•Competitive
Strategy Options
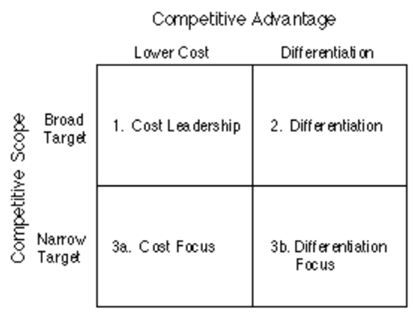
- Cost Leadership: Cost leadership, basically, means the lowest cost of operation in the industry. Cost leadership is often driven by company efficiency, size, scale, scope and cumulative experience.
- Differentiation: the development of a product or service that offers unique attributes that are valued by customers and that customers perceive to be better than or different from the products of the competition.
- Focus (Niche): describes enterprise strategies that are focused closely on serving segment-specific or niche markets. Business strategy may alternatively be based on the process of product or service differentiation across a range of markets and market segments.
- Cost Leadership: Cost leadership, basically, means the lowest cost of operation in the industry. Cost leadership is often driven by company efficiency, size, scale, scope and cumulative experience.
- Differentiation: the development of a product or service that offers unique attributes that are valued by customers and that customers perceive to be better than or different from the products of the competition.
- Focus (Niche): describes enterprise strategies that are focused closely on serving segment-specific or niche markets. Business strategy may alternatively be based on the process of product or service differentiation across a range of markets and market segments.
Competitive
Strategy Options
•A
firm's relative position within its industry determines whether a firm's
profitability is above or below the industry average. The fundamental basis of
above average profitability in the long run is sustainable competitive
advantage. There are two basic types of competitive advantage a firm can
possess: low cost or differentiation. The two basic types of competitive
advantage combined with the scope of activities for which a firm seeks to
achieve them, lead to three generic strategies for achieving above average
performance in an industry: cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. The
focus strategy has two variants, cost focus and differentiation focus.

Porter’s
Value Chain
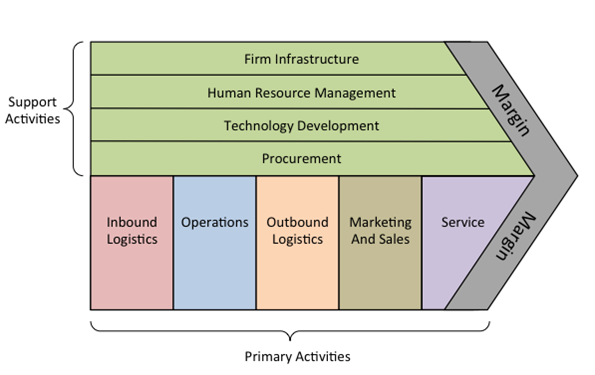
Primary
Activities
1.Inbound
Logistics - involve relationships with suppliers and include all the
activities required to receive, store, and disseminate inputs.
2.Operations -
are all the activities required to transform inputs into outputs (products and
services).
3.Outbound
Logistics - include all the activities required to collect, store, and
distribute the output.
4.Marketing
and Sales - activities inform buyers about products and services, induce
buyers to purchase them, and facilitate their purchase.
5.Service -
includes all the activities required to keep the product or service working
effectively for the buyer after it is sold and delivered.
Secondary
Activities
1.Procurement - is the acquisition of
inputs, or resources, for the firm.
2.Human Resource management - consists
of all activities involved in recruiting, hiring, training, developing,
compensating and (if necessary) dismissing or laying off personnel.
3.Technological Development - pertains
to the equipment, hardware, software, procedures and technical knowledge
brought to bear in the firm's transformation of inputs into outputs.
4.Infrastructure - serves the
company's needs and ties its various parts together, it consists of functions
or departments such as accounting, legal, finance, planning, public affairs,
government relations, quality assurance and general management.
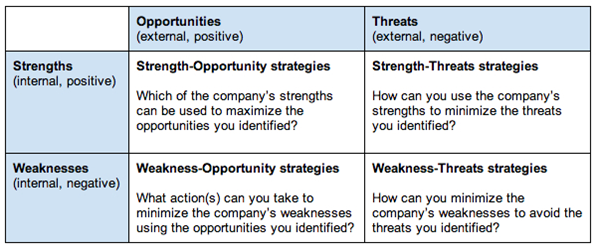
SWOT
Analysis
SWOT Analysis is a useful technique for understanding your Strengths and Weaknesses, and for identifying both the Opportunities open to you and the Threats you face.
Last modified: Tuesday, August 14, 2018, 8:31 AM
