Reading: Debt Management Ratios
Debt
Management Ratios
Debt Management Ratio is a computation that is a computation that is used to measure a company’s ability to pay its long term debt obligations
Payables
Turnover
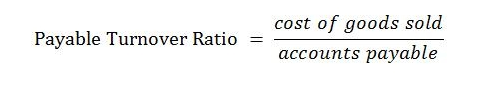
Company A
COGS = $1,000,000
Accounts Payable = $506,000
Payables Turnover = $1,000,000
$506,000
Age
of Payables

Age of Payables = 365
1.97
Age of Payables = 185 days
Debt
to Asset Ratio
Total Assets
Total Assets = $3,373
Current Liabilities = $543
Long Term Debts = $531
Debt to Assets = $543
+ $531
$3,373
Debt to Assets = 31.84%
Debt
to Equity Ratio
Total Equity
Total Equity = $2,299
Current Liabilities = $543
Long Term Debts = $531
Debt to Equity = $543
+ $531
$2,299
Debt to Equity = 46.72%
Times
Interest Earned
Times Interest Earned Ratio = Earnings
before Interest and Taxes
Interest Expense
Interest Expense = $141
TIE = $691
$141
TIE = 4.9 times
