Reading: Restructuring Through Bankruptcy
Bankruptcy
•Bankruptcy
can be a creative corporate finance tool. Reorganization through the bankruptcy
process can in certain instances provide unique benefits that are unattainable
through other means.
•Clearly,
bankruptcy is a drastic step that is only pursued when other more favorable
options are unavailable. A bankruptcy filing is an admission that a company has
in some way failed to achieve certain goals.
Bankruptcy
Overview
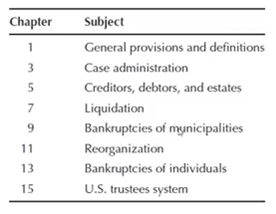
The Bankruptcy Act of 1978 (the Bankruptcy Code) is the main bankruptcy law of the United States. It organizes bankruptcy laws into eight odd-numbered chapters.
Economic
Failure
•Economic
failure is the more ambiguous. For example, economic failure could mean that
the firm is generating losses; that is, revenues are less than costs.
•However
depending on the users and the context, economic failure could also mean that
the rate of return on investment is less than the cost of capital. It could
also mean that the actual returns earned by a firm are less than those that
were forecast.
Financial
Failure
•Financial
failure is less than ambiguous than economic failure. Financial failure means
that a company cannot meet its current obligations as they come due. The
company does not have sufficient liquidity to satisfy its current liabilities.
Causes
of Business Failure
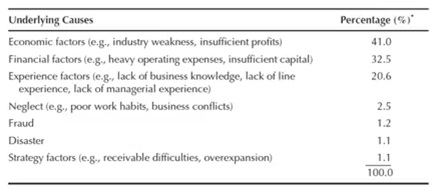
•The
three most common factors of business failure were economic factors, such as
weakness in the industry; financial factors, such as inefficient
capitalization; and weaknesses in managerial experience, such as insufficient
managerial knowledge.
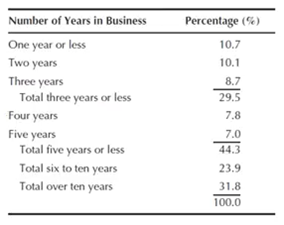
•Research
analysis shows that 10.7% of businesses failed in one year or less. Just under
one-third of the companies were in business for three years or less, where as
44.3% existed up to five years.
Causes
of Financial Distress
•Financial
distress and bankruptcy have been linked to many of the highly leveraged deals
that took place in the 1980’s.
•Studies
have been conducted of a study of 29 leveraged recapitalizations that took
place between 1984 and 1988. They defined leveraged recapitalizations as
transactions that use proceeds from new debt obligations to make payouts to
shareholders. The results show that 31% of the firms that completed leveraged
recapitalizations encountered financial distress.
Chapter
11 Reorganization
•The
purpose of the reorganization section (Chapter 11) of the Bankruptcy Code is to
allow a reorganization plan to be developed that will allow the company to
continue to operate. This plan will contain the changes in the company that its
designers believe are necessary to convert it to a profitable entity.
•If
a plan to allow the profitable operation of the business cannot be formulated,
the company may have to be liquidated, with its assets sold and the proceeds
used to satisfy the company’s liabilities.
Benefits
of Chapter 11 Process for the Debtor

Chapter
7 - Liquidation
•Liquidation
is a distressed firm’s most drastic alternative, and it is usually pursued only
when voluntary agreement and reorganization cannot be successfully implemented.
In a liquidation, the company’s assets are sold and the proceeds are used to
satisfy claims, priority as follows:

Last modified: Tuesday, August 14, 2018, 8:43 AM
